Bandwidth search¶
To find out the optimal bandwidth, gwlearn provides a BandwidthSearch class, which trains models on a range of bandwidths and selects the most optimal one.
import geopandas as gpd
from geodatasets import get_path
from gwlearn.ensemble import GWRandomForestClassifier
from gwlearn.linear_model import GWLinearRegression
from gwlearn.search import BandwidthSearch
Get sample data
gdf = gpd.read_file(get_path("geoda.ncovr")).to_crs(5070)
gdf['point'] = gdf.representative_point()
gdf = gdf.set_geometry('point')
y = gdf["FH90"]
X = gdf.iloc[:, 9:15]
Interval search¶
Interval search tests the model at a set interval.
search = BandwidthSearch(
GWLinearRegression,
geometry=gdf.geometry,
fixed=False,
n_jobs=-1,
search_method="interval",
min_bandwidth=50,
max_bandwidth=1000,
interval=100,
criterion="aicc",
verbose=True,
)
search.fit(
X,
y,
)
Bandwidth: 50.00, aicc: 15666.353
Bandwidth: 150.00, aicc: 15498.936
Bandwidth: 250.00, aicc: 15660.999
Bandwidth: 350.00, aicc: 15775.129
Bandwidth: 450.00, aicc: 15854.287
Bandwidth: 550.00, aicc: 15918.673
Bandwidth: 650.00, aicc: 15975.564
Bandwidth: 750.00, aicc: 16031.276
Bandwidth: 850.00, aicc: 16080.155
Bandwidth: 950.00, aicc: 16126.986
<gwlearn.search.BandwidthSearch at 0x17f353bc0>
The scores_ series then contains the AICc, selected as the criterion, which can be plotted to see the change of the model performance as the bandwidth grows.
search.scores_.plot()
<Axes: >
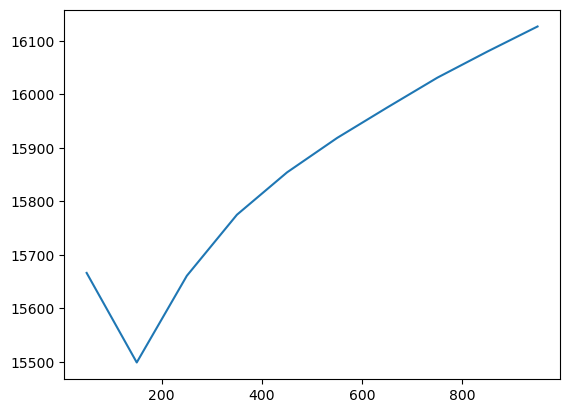
The optimal bandwidth is then the lowest one.
search.optimal_bandwidth_
np.int64(150)
Golden section¶
Alternatively, you can try to use the golden section algorithm that attempts to find the optimal bandwidth iteratively. However, note that there’s no guaratnee that it will find the globally optimal bandwidth as it may stick to the local minimum.
search = BandwidthSearch(
GWLinearRegression,
geometry=gdf.geometry,
fixed=True,
n_jobs=-1,
search_method="golden_section",
criterion="aicc",
min_bandwidth=250_000,
max_bandwidth=2_000_000,
verbose=True,
)
search.fit(
X,
y,
)
Bandwidth: 918447.5, score: 16135.833
Bandwidth: 1331552.5, score: 16367.508
Bandwidth: 663120.61, score: 15901.394
Bandwidth: 505326.89, score: 15734.258
Bandwidth: 407799.68, score: 15644.228
Bandwidth: 347527.21, score: 15599.261
Bandwidth: 310274.74, score: 15585.033
Bandwidth: 287252.47, score: 15579.996
Bandwidth: 273023.14, score: 15583.440
Bandwidth: 296045.75, score: 15580.453
Bandwidth: 281817.09, score: 15580.952
Bandwidth: 290610.83, score: 15579.452
Bandwidth: 292686.98, score: 15579.549
Bandwidth: 289328.29, score: 15579.566
Bandwidth: 291404.06, score: 15579.440
Bandwidth: 291893.95, score: 15579.458
Bandwidth: 291100.94, score: 15579.438
<gwlearn.search.BandwidthSearch at 0x331d955b0>
You can see how the agorithm searches and iteratively gets closer to the optimum.
search.optimal_bandwidth_
np.float64(291100.9431339667)
Other metrics¶
By default, BandwidthSearch computes AICc, AIC and BIC, available through metrics_.
search.metrics_
| aicc | aic | bic | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9.184475e+05 | 16135.832631 | 16132.605473 | 16556.503755 |
| 1.331552e+06 | 16367.507618 | 16366.574492 | 16597.123551 |
| 6.631206e+05 | 15901.393868 | 15891.545192 | 16623.552420 |
| 5.053269e+05 | 15734.258373 | 15708.559009 | 16874.775997 |
| 4.077997e+05 | 15644.228226 | 15588.888391 | 17273.283311 |
| 3.475272e+05 | 15599.260550 | 15500.960777 | 17709.892539 |
| 3.102747e+05 | 15585.032697 | 15436.700466 | 18110.784586 |
| 2.872525e+05 | 15579.995539 | 15383.747794 | 18423.649729 |
| 2.730231e+05 | 15583.440146 | 15347.827157 | 18650.241701 |
| 2.960457e+05 | 15580.452736 | 15404.583147 | 18296.148267 |
| 2.818171e+05 | 15580.952181 | 15370.724573 | 18507.176295 |
| 2.906108e+05 | 15579.451964 | 15391.351712 | 18373.091183 |
| 2.926870e+05 | 15579.548602 | 15396.249687 | 18343.014101 |
| 2.893283e+05 | 15579.566286 | 15388.413516 | 18392.115393 |
| 2.914041e+05 | 15579.439825 | 15393.191365 | 18361.504693 |
| 2.918940e+05 | 15579.458231 | 15394.342859 | 18354.402006 |
| 2.911009e+05 | 15579.438393 | 15392.484736 | 18365.920248 |
You can also ask for a log loss and even use it as a criterion for the selection. This is useful when comparing classification models with varying prediction rate (you can also retrieve that for each bandwidth).
search = BandwidthSearch(
GWRandomForestClassifier,
geometry=gdf.geometry,
fixed=False,
n_jobs=-1,
search_method="interval",
min_bandwidth=50,
max_bandwidth=1000,
interval=100,
metrics=['log_loss', 'prediction_rate'],
criterion="log_loss",
verbose=True,
)
search.fit(
X,
y > y.median(), # simulate binary categorical variable
)
Bandwidth: 50.00, log_loss: 0.568
Bandwidth: 150.00, log_loss: 0.550
Bandwidth: 250.00, log_loss: 0.578
Bandwidth: 350.00, log_loss: 0.617
Bandwidth: 450.00, log_loss: 0.593
Bandwidth: 550.00, log_loss: 0.553
Bandwidth: 650.00, log_loss: 0.494
Bandwidth: 750.00, log_loss: 0.524
Bandwidth: 850.00, log_loss: 0.555
Bandwidth: 950.00, log_loss: 0.571
<gwlearn.search.BandwidthSearch at 0x30be6d370>
Log loss is then part of the metrics.
search.metrics_
| aicc | aic | bic | log_loss | prediction_rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | NaN | 14260.458748 | 47847.673185 | 0.568032 | 0.663533 |
| 150 | 6152.053899 | 4482.927615 | 10277.629979 | 0.549784 | 0.727391 |
| 250 | 3894.720134 | 3628.636942 | 6452.220177 | 0.577733 | 0.747164 |
| 350 | 3624.008863 | 3543.537156 | 5240.691021 | 0.617262 | 0.784441 |
| 450 | 3498.456652 | 3457.505985 | 4743.376262 | 0.593468 | 0.832415 |
| 550 | 3303.210326 | 3278.050284 | 4322.854246 | 0.552747 | 0.864182 |
| 650 | 3034.904706 | 3017.896184 | 3905.122425 | 0.493768 | 0.897245 |
| 750 | 3258.804907 | 3246.121567 | 4034.695415 | 0.523635 | 0.930308 |
| 850 | 3524.552076 | 3514.813454 | 4226.823882 | 0.555048 | 0.967585 |
| 950 | 3705.116372 | 3697.267706 | 4352.457033 | 0.570866 | 1.000000 |
And is reported directly as score as it is set as the criterion.
search.scores_.plot()
<Axes: >
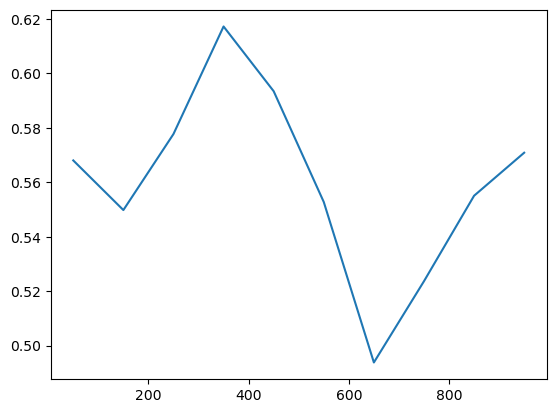
As a result, the optimal bandwidth is derived directly from it.
search.optimal_bandwidth_
np.int64(650)